In a software development environment where agility and speed are table stakes, the onset of application development platforms from enterprise solution providers can offer a dynamic channel to grow the business.

Part One of Three-Part Series
The cost of software failures in the US is staggering at over $1 Trillion a year1. The causes of such failures are many but are primarily driven by changing requirements during implementations, lack of proper documentation, and insufficient testing/quality of engineering.
In many cases, development teams are tasked with building complete solutions without adequate support on architecture and design. Developers are often forced to work with undocumented procedures and design philosophies to guide their development. It results in massive inefficiencies, slower responses to needs, and cost over-runs for an enterprise.
In recent years application development platforms (ADP) from enterprise solution providers have risen in prominence. These are designed to help application developers in designing, developing, and deploying applications faster and more efficiently than ‘going it alone.’ An application development platform can assist in responding to fast-changing business requirements in a more agile and efficient manner.
There have been several developments that have led to the growth of ADP’s:
- The proliferation of a disruptive class of tools enabling non-programmers to build applications:
Rapid Application Development (RAD) (low code/no code) technology has emerged as a highly interactive application development approach that helps build software applications rapidly. The global market for rapid application development platforms is expected to grow from US$ 7.76 billion in 2018 to US$ 46.16 billion in 2023 at a CAGR of 42.9%2. 23% of enterprise development teams were using low-code platforms in 2018, and another 22% planned to do so in 20193. Growing adoption of low-code platforms has enabled organizations to accelerate their digital innovation and transformation initiatives, improve the responsiveness of their IT function and reduce the dependency of their application development function on technical resources with limited availability in the market. - Significant investments in digital platform infrastructure:
Enterprise solution companies are actively investing in application development platforms. They are deploying an extensive amount of core domain APIs to accelerate initiatives on the cloud, IoT, and digital enterprise solutions. A few companies are engaging in acquisition of capabilities to accelerate development lifecycle. Examples include Siemens, which acquired Mendix, a low-code application platform to strengthen its digital enterprise leadership and General Electric (GE), which acquired IQP corporation to integrate its code-free application to Predix platform for IIoT.
The complexity of today’s business environment has made it more challenging than ever for independent software vendors (ISVs) and system integrators (SIs) to develop and market applications. A new approach requires them to simplify their operations and infrastructure requirements and allows them to leverage external capabilities to expedite the processes internally.
As discussed, many enterprise solution providers have spent the last several years, both acquiring and building capabilities to bring platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offerings to the market. It has created an opportunity for ISVs and SIs to leverage best-in-class features and functionalities to speed up the development process and create a channel for partnerships and sales. These best-in-class features include:
- Open-source platform: Open-source applications have a flexible and adaptive approach towards application development. With source code being available in the public domain, specific functional code would be reviewed & maintained by more than a certain group of developers, which minimizes issues & loopholes.
- A broad set of domain APIs: APIs are the connective tissue in today’s ecosystems. Once limited mainly to technical domains, they have now become a significant engine to accelerate business domain capabilities. An extensive range of APIs help in building robust portfolios to maximize consumer and business impact. Large solution vendors are going to market with a clear business-backed strategy and a monetization model for APIs. These APIs will be used to drive adoption and enable new avenues for revenue growth and value.
- Flexible access to development options: Users can get high-code options through APIs or access to a low-code, rapid application development platform that allows anyone to build/deploy apps for a specific workplace to any infrastructure.
Business implication of next-generation Application Development Platforms on ISVs and SIs
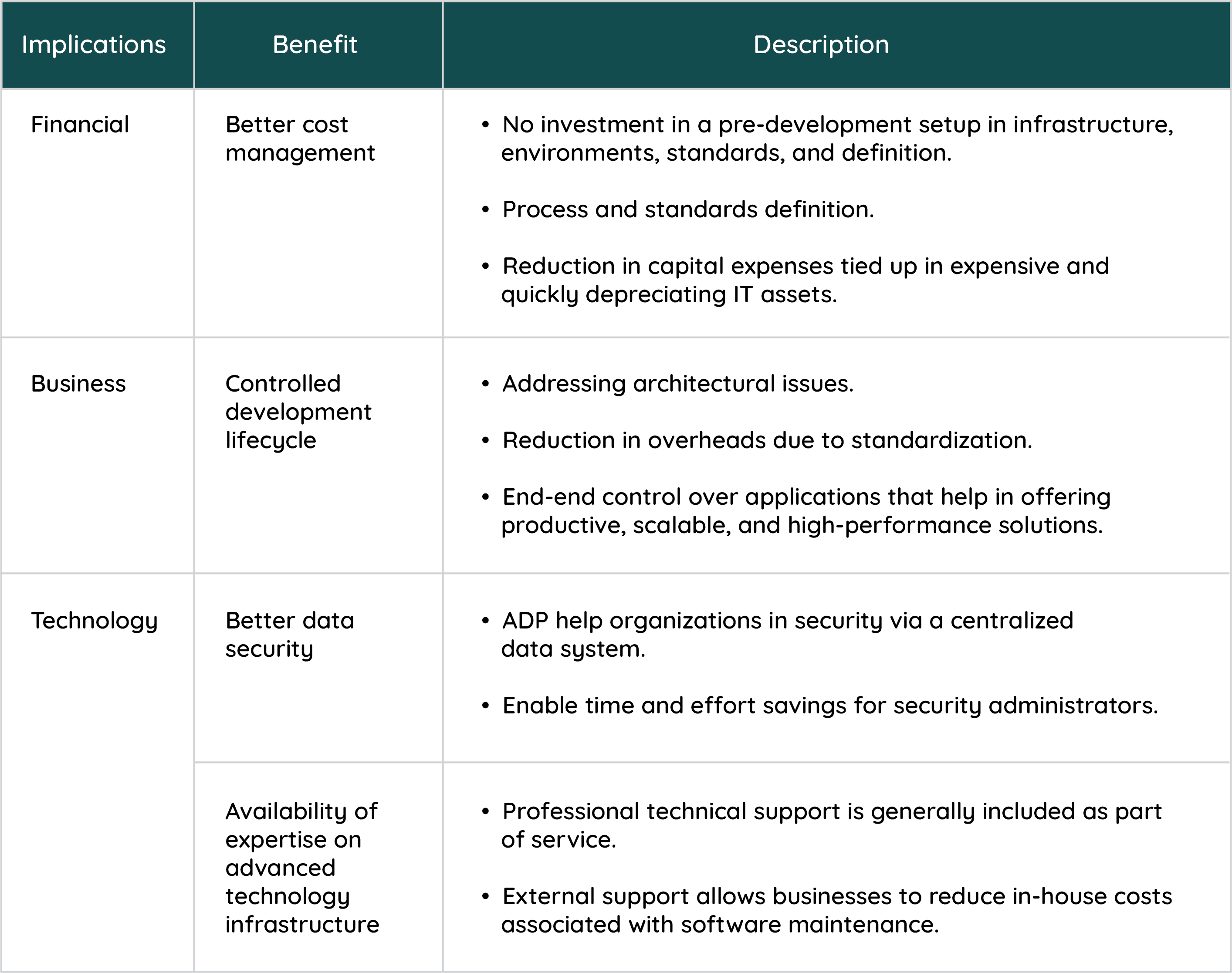
In subsequent blogs, we’ll be addressing both the potential inhibitors and business benefits of partnering with an enterprise solution provider on their application development platform.
For access to the research that fueled this blog, click here.
-------------
1. Consortium for IT Software Quality (CISQ)
2. Research and Markets
3. Forrester





